As industries and consumers become increasingly aware of environmental responsibility, the demand for sustainable building materials is rising. Among all modern materials, aluminum stands out as one of the most effective in reducing carbon emissions and supporting eco-friendly construction. From production and transportation to usage and recycling, aluminum helps lower environmental impact at every stage of its lifecycle.
Understanding Carbon Footprint in Construction
A carbon footprint refers to the total amount of greenhouse gas emissions, especially carbon dioxide (CO₂), produced during the lifecycle of a product. In construction and manufacturing, emissions come from:
- Raw material extraction
- Manufacturing processes
- Transportation and installation
- Maintenance and replacement
- Disposal or recycling
Choosing the right material can significantly reduce emissions—and aluminum plays a major role here.
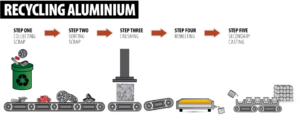
1. 100% Recyclable Without Loss of Quality
One of aluminum’s greatest environmental advantages is that it is fully recyclable. Aluminum can be recycled repeatedly without losing its strength, durability, or performance.
Unlike many materials that degrade during recycling, recycled aluminum performs just as well as newly produced metal. This supports a circular economy, where materials are reused instead of discarded.
2. Extremely Energy-Efficient Recycling Process
Recycling aluminum requires up to 95% less energy than producing primary aluminum from raw bauxite ore. This drastic energy reduction results in:
- Lower greenhouse gas emissions
- Reduced fossil fuel consumption
- Conservation of natural resources
As a result, aluminum recycling is one of the most energy-efficient industrial processes available today.
3. Lightweight Material Means Lower Transport Emissions
Aluminum is significantly lighter than steel and other traditional metals. This lightweight property reduces fuel consumption during:
- Transportation from factories to construction sites
- Handling and lifting during installation
Fewer heavy loads mean fewer transport trips and lower fuel usage—directly reducing carbon emissions.
4. Long Lifespan Reduces Resource Consumption
Aluminum products are known for their long service life. They resist corrosion, weather damage, and structural degradation, even in harsh environments.
Because aluminum lasts for decades:
- Fewer replacements are required
- Less raw material is consumed
- Construction waste is reduced
This durability significantly lowers environmental impact over time.
5. Supports Energy-Efficient Buildings
Modern aluminum systems are designed to work with thermal break technology, insulated glazing, and airtight sealing systems. These features improve insulation and help:
- Reduce heat loss during winter
- Minimize heat gain during summer
- Lower energy demand for heating and cooling
By improving building energy efficiency, aluminum helps reduce ongoing operational carbon emissions.
6. Minimal Maintenance, Lower Environmental Impact
Unlike steel, aluminum does not require frequent repainting, rust-proofing, or chemical treatments. Reduced maintenance means:
- Fewer harmful chemicals released into the environment
- Lower energy and material consumption
- Reduced long-term emissions
This makes aluminum a cleaner and more environmentally responsible choice.
7. High Reuse and End-of-Life Value
At the end of its lifecycle, aluminum retains significant value and is highly sought after for recycling. Instead of becoming landfill waste, aluminum products are:
- Collected
- Reprocessed
- Reused in new applications
This reduces landfill pressure and supports sustainable material management.
Applications of Sustainable Aluminum
Aluminum is widely used in environmentally conscious projects, including:
- Residential and commercial buildings
- Windows, doors, and façades
- Structural and architectural systems
- Transportation and industrial sectors
Its sustainability benefits extend across multiple industries.
Conclusion: A Smarter Choice for a Greener Future
Aluminum is more than just a lightweight and durable material, it is a key contributor to reducing carbon footprint. Its recyclability, energy-efficient processing, long lifespan, and support for energy-efficient buildings make it one of the most sustainable materials available today.
By choosing aluminum, individuals and industries take an important step toward lower emissions, responsible resource use, and a cleaner future.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
1. Why is aluminum considered an eco-friendly building material?
Aluminum is eco-friendly because it is 100% recyclable, energy-efficient to reuse, lightweight for transport, and long-lasting. These qualities significantly reduce carbon emissions across its entire lifecycle.
2. Does recycling aluminum really reduce carbon emissions?
Yes. Recycling aluminum uses up to 95% less energy than producing new aluminum from raw ore, which results in a substantial reduction in greenhouse gas emissions.
3. How does aluminum compare to steel in terms of carbon footprint?
Aluminum generally has a lower lifecycle carbon footprint than steel due to its lighter weight, lower transportation emissions, corrosion resistance, and superior recyclability.
4. Can aluminum help make buildings more energy-efficient?
Absolutely. Aluminum systems support thermal breaks, insulated glazing, and airtight designs, which reduce heat loss and lower energy consumption for heating and cooling.
5. Does aluminum require environmentally harmful maintenance?
No. Aluminum does not rust or corrode, so it does not need frequent repainting or chemical treatments, reducing long-term environmental impact.
6. How does aluminum’s lightweight nature reduce emissions?
Because aluminum is lighter than most metals, it requires less fuel for transportation and handling, leading to lower CO₂ emissions during logistics and installation.
7. What happens to aluminum at the end of its lifecycle?
Aluminum is collected and recycled instead of being discarded as waste. It retains high value and is reused in new products, supporting a circular economy.
8. Is recycled aluminum as strong as new aluminum?
Yes. Recycled aluminum maintains the same strength, durability, and performance as primary aluminum, making it equally suitable for construction and architectural use.
9. Does using aluminum reduce construction waste?
Yes. Aluminum’s durability and reusability reduce the need for replacements and repairs, leading to less construction and demolition waste over time.
10. Which construction applications benefit most from sustainable aluminum?
Aluminum is ideal for windows, doors, curtain walls, roofing systems, and structural components where durability, energy efficiency, and sustainability are essential.